- Motion Realizing
- info@neuromove.it
Core training applied to young players: some practical proposals.

game
#CORETRAINING #COREREGION #INSTABILITYTRAINING #CATENECINETICHE #FITBALL #BOSU #KALCIO #FOOTBALL #EQUILIBRIO #FORZA #PROPOSTAPRATICA #PROPRIOCEZIONE #KIDTRAINING #CHILDREN #STABILITY
INTRODUCTION
The following thesis will address the theme of core understood as a functional anatomical structure located in the central region of the body, in particular it will first explore the topic of training in this area in a general sense, then going more specifically by applying it to the world of football in particular to the youth sector.
Today we know that a core region developed is closely related to more brilliant sports performance, and more importantly to the decrease in the frequency of injuries, as well as to an improvement in the quality of life of the subjects if we talk about prevention, and in our case, try to familiarize children with this type of training, laying a solid foundation for subsequent body growth.
ANATOMICAL BASICS
- Anterior muscles: rectus abdominis, internal oblique, external oblique, transverse abdomen,
- Posterior muscles: erectors of the spine, lumbar multifidus, buttock
-Other mentions: diaphragm muscle, pelvic floor muscles.
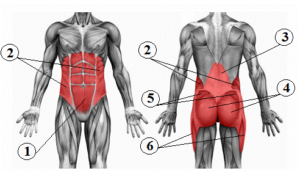
All this muscular complex contributes to forming a sort of "cylindrical muscular box" which if it contracts with a certain synergy determines the shrinkage of this box and therefore a compression, this would give more stability to the body and protection for the delicate lumbar area which as we know is subject to various injuries.
PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS AND BIOMECHANICAL
It is possible to state that all movements follow pre-established lines of force, determined by the so-called kinetic chains.
These are nothing more than muscle chains that work sequentially for the propagation of the organizing forces of the body. In particular, there are crossed kinetic chains, which connect the right and left side of the body, for example for the torsion movement of the bust and straight kinetic chains, responsible to a greater extent for the stability of the body and its static nature; these collaborate with each other in the dynamics of movement and postural balance.
With these assumptions we can say that during a complex movement, which may be an athletic gesture as kicking a ball or throwing a ball, the job is not done by a muscle only or a few muscles, but we must consider the movement as a result of the collaboration of sopracitate kinetic chains.
The region core in particular, being in a central position, it is involved in the passage of almost all of these chains; that's why develop correctly it allows a transmission of force between the kinetic chains decidedly more optimal, and therefore to suffer will be the movements of all the days and sports gestures.
WORK OUT
training the core means improving the strength of this region and also potentiate the neuromuscular control; the conditioning of the muscles of the protocols core They are well known and practiced by all people of all ages and levels.
In recent years he has become increasingly marked the workout that involves the use of unstable surfaces as can be fitball, Swissball, proprioceptive boards, bosu etc ... These means are intended to coach the individual proprioception etc .. The principle on which is based this methodology is the destabilizing effect that the unstable base provides to the subject, which consequently will "stress" and stimulate the neuromuscular system more pronounced, resulting in an even greater muscle activation mode.
There are many studies that confirm this in this regard may come in handy contributions from Vera-Garcia et F.J all. (7): by electromyography (EMG) has been possible to assess the level of muscle activation of the districts of core during the execution of movements with fitball crunch and without. It has been shown that activation of the core It is much higher when we include the instability.

crunch normale

crunch instabile su fitball
EXERCISES BASIC
PLANK: Exercise that must be more effectively stimulate the anterior portion of the core region (rectum, transverse, oblique)
SIDE PLANK: Exercise that goes to stimulate lateral muscles more

HAMSTRING BRIDGE: Exercise that goes to recruit and stimulate the gluteal muscles and the hamstring muscles.

FOOTBALL AND CORE
WHY 'TRAIN THE CORE REGION AND THE BALANCE OF A PLAYER?
First, as previously specified, have a core well developed allows the player to incur less frequently in accidents that can pregiudicargli the racing season. He said in fact that with a core weak, and therefore a more precarious balance and a transmission of force in the lower limbs less efficient, increased the athlete's exposure to load injuries of the lower limb structures. Nowadays it is very important at a competitive level and at lower levels to ensure a seal during the whole year. Secondly properly train the core also means a better performance in the field; if we read the prestativo model of football we see how it is dotted with demands to stimulate the balance of the player.
Digging into the technical part, have a core and developed a good balance means you have more stability during jumps, as it can be in a melee in the area to try to hit the ball head; during acceleration, deceleration and direction changes, the central muscles is very stimulated.
Even during hectic period as blends and contrasts, a player with a more developed stabilizer muscles is more likely to emerge victorious if we leave out the technical skills.
PROPOSAL FOR PRACTICE
GENERAL EXERCISE OF STRENGTH AND BALANCE FOR CHILDREN
Before going into the practical proposal, it is good to explore the theme dell'allenabilità strength in children.
On this issue linger many false beliefs that claim that strength training can go to destabilize and undermine the proper muscle and skeletal growth in children.
This may be true if the latter are proposed bearing exercises with free weights or with excessive unilateral loads.
Administer wrong loads in young people can increase primarily the risk of fractures and various types of trauma, but also by stimulating excessive production of testosterone, facilitate the premature fusion of the epiphyseal discs of long bones. This translates into a slowdown nell'accrescimento bones and less growth in height.
To avoid these situations, it is good that the coach has in mind the sensitive stages of development in the child, not to exceed the administration load. That said, it can be said that exercises done without any load and without excessive repetitions give the stimulus to the child for the development of strength, stability and balance in adolescence and adulthood.
Specifically, if we focus on balance and strength of the stabilizer muscles in children, there are several scientific evidence confirming that the inclusion of balance training exercises in a workout plan for children is favorable according to several aspects.
In this regard it is interesting to mention the recent study Wälchli M. Et all. (19): the authors ask in what way and to what extent the young age affect training results; to answer this question, they undergo five weeks of balance training groups of subjects divided into basic training at different ages, then comparing them with the control group, which however does not receive any type of balance training.
The results showed in subjects trained an improvement in postural dynamics, particularly in the younger age group, and overall increased strength and decreased postural deficit.
This study shows for the first time that the postural control can also be trained in children six years of age, and that this helps to improve their balance.
PROPOSAL FOR PRACTICE
The proposal of this thesis aims to provide practical solutions applicable to children in order to improve balance, strength of the central muscles, and decrease the incidence of injuries, as well as to build a solid framework for when the baby will grow for harmonious development of the body.
The main goal is to approach the children with basic postures activation of muscles core through games, also they will be offered exercises that stimulate balance, balance exercises monopodalic etc ...
The exercises will use as a football background but as mentioned earlier this will be applicable to any other sport.
PROPOSAL OF SOME YEARS (WORK IN PROGRESS)
EXERCISE 1
CONDUCT The exercise will be in pairs: one remains in the deck in front of another, the latter will have to throw the ball so try to pass it under the bridge formed by Comrade.
OPTIONS
-passaggio with your hands;
-passaggio with their feet;
-conduzione arrest and passage.
PURPOSE The active year, mainly the isometrically the region of the front core Student that is bridged secondly refines the accuracy of passage mate with the ball.
EXERCISE 2
CONDUCT Exercise, which takes place in pairs, simulates the reverse crunch, a student is lying supine position with knees flexed and a ball between the feet with a reverse crunch movement by keeping the knees bent will have to pass the ball to mate that stopperà the ball the fly and run through the ball will have to bring the ball to his lying.
PURPOSE To develop the muscles of the core with a certain dynamism to the other students hone the stop ball and run.
EXERCISE 3
CONDUCT Exercise in pairs the first student launches a circle the other jump in the vicinity of this with one leg trying to stay in balance with a single support, the other will launch the ball and the pupil in equilibrium will have to try to make a passage on the fly, once this is done will be launched a second circle on which the student will jump with the limb with which previously hit the ball.
PURPOSE The exercise It stimulates the dynamic balance and by the support given static mono breech also the passage of the ball makes it more specific as it is used to the pupil to the ball passage in precarious equilibrium conditions, frequent situation in a football game, hitting in an alternating manner with the right foot and left It stimulates the bilateral nature of the gesture.
CONCLUSION
L 'training with the purpose of improving the stability of the core and the balance is ideal for any subject and in a sporting context and rehabilitation, has also been proven as it actually is, concomitant use of these exercises for children.
This fact may be important to create the proper conditions for a good muscular development during sensitive phases of child growth.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
-Vera-Garcia FJ, Grenier SG, McGill SM. ”Abdominal muscle response during curl-ups on both stable and labile surfaces”. Phys Ther 2000;80: 564-569
–Wälchli M, Ruffieux J, Mouthon A, Keller M, Taube W. “Is Young Age a Limiting Factor When Training Balance? Effects of Child-Oriented Balance Training in Children and Adolescents”. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2018 Feb 1;30(1):176-184